okhttp核心流程分析
type
Post
status
Published
date
Dec 28, 2021
slug
okhttp
summary
来源:原创
tags
Android
category
码农
icon
password
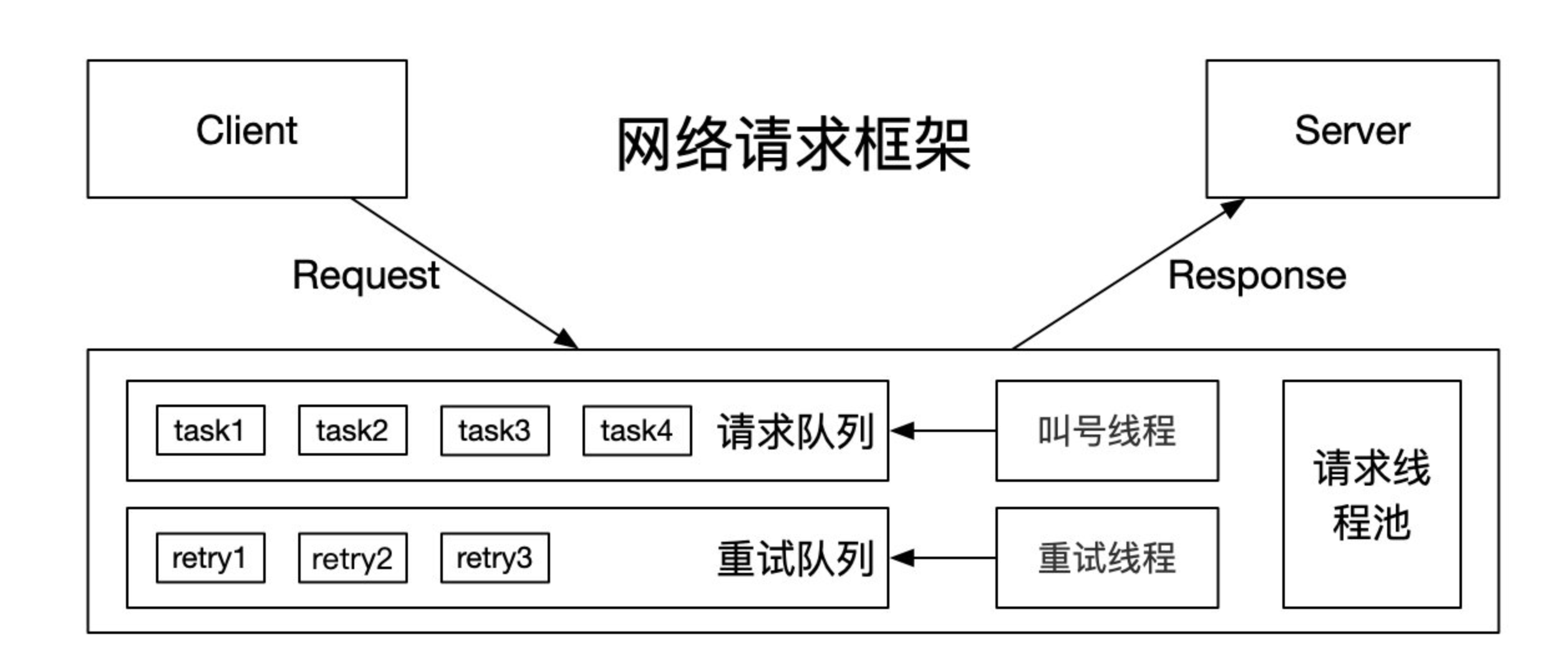
上图为常见网络请求框架,
okhttp3 网络框架也和上图类似,下面开始具体分析。简单使用
Request request = new Request.Builder().url("<http://www.baidu.com>").get().build(); Call call = client.newCall(request); call.enqueue(new Callback() { @Override public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) { System.out.println("Fail"); } @Override public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException { System.out.println(response.body().string()); } });
call.enqueue方法会调用dispatch的enqueue方法。
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) { if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) { runningAsyncCalls.add(call); executorService().execute(call); } else { readyAsyncCalls.add(call); }
dispatch分发请求
dispatch分发请求。
/** Executes calls. Created lazily. */ private @Nullable ExecutorService executorService; /** Ready async calls in the order they'll be run. */ private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>(); /** Running asynchronous calls. Includes canceled calls that haven't finished yet. */ private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>(); /** Running synchronous calls. Includes canceled calls that haven't finished yet. */ private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
dispatch主要维护以上几个队列,将每个请求添加到队列/从队列中移除。
队列中的请求通过线程池executorService来执行。
最后会调用到AsyncCall的execute()方法中,
@Override protected void execute() { boolean signalledCallback = false; try { Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(); if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) { signalledCallback = true; responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled")); } else { signalledCallback = true; responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response); } } catch (IOException e) { if (signalledCallback) { // Do not signal the callback twice! Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e); } else { eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e); responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e); } } finally { client.dispatcher().finished(this); } }
最后**getResponseWithInterceptorChain();**调用一系列拦截器完成网络请求。
拦截器
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException { // Build a full stack of interceptors. List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors()); interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor); interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar())); interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache())); interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client)); if (!forWebSocket) { interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors()); } interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket)); Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0, originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(), client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis()); return chain.proceed(originalRequest); }
- *chain.proceed()方法中调用Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);**处理拦截器逻辑和调用下一个proceed()。
依次循环,完成一次网络情况,并返回response。
okhttp自带拦截器
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor
重试和重定向拦截器。
另外,该拦截器会创建一个streamAllocation对象,该对象会在ConnectInterceptor中使用。
streamAllocation = new StreamAllocation(client.connectionPool(), createAddress(request.url()), call, eventListener, callStackTrace);
BridgeInterceptor
桥接拦截器,主要用来添加请求头部等信息。
CacheInterceptor
缓存拦截器,主要用来添加/读取请求缓存,包括head和body。
ConnectInterceptor
连接拦截器。
首先会获取stramAllocation对象实例,该对象在RetryAndFollowUpIntercepter拦截器中创建。
HttpCodec httpCodec = streamAllocation.newStream(client, chain, doExtensiveHealthChecks); RealConnection connection = streamAllocation.connection();
以上为该拦截器最重要的两行代码,先来看第一行:
public HttpCodec newStream( OkHttpClient client, Interceptor.Chain chain, boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks) { int connectTimeout = chain.connectTimeoutMillis(); int readTimeout = chain.readTimeoutMillis(); int writeTimeout = chain.writeTimeoutMillis(); boolean connectionRetryEnabled = client.retryOnConnectionFailure(); try { RealConnection resultConnection = findHealthyConnection(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, connectionRetryEnabled, doExtensiveHealthChecks); HttpCodec resultCodec = resultConnection.newCodec(client, chain, this); synchronized (connectionPool) { codec = resultCodec; return resultCodec; } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RouteException(e); } }
newStream方法中会获取一个RealConnection对象,并对该对象进行编码后返回。
RealConnection resultConnection = findHealthyConnection(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, connectionRetryEnabled, doExtensiveHealthChecks); HttpCodec resultCodec = resultConnection.newCodec(client, chain, this);
findHealthyConnection方法又回调用findConnection方法,由方法注释可知该方法会先从connectionPool检查是否有可复用的Connection,如果存在则复用,不存在则创建一个。
/** * Returns a connection to host a new stream. This prefers the existing connection if it exists, * then the pool, finally building a new connection. */ private RealConnection findConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws IOException { boolean foundPooledConnection = false; RealConnection result = null; Route selectedRoute = null; Connection releasedConnection; Socket toClose; synchronized (connectionPool) { /** ** 省略一些代码,主要是检测异常及connectionPool中是否有可复用的Connection **/ if (result != null) { // If we found an already-allocated or pooled connection, we're done. return result; } /** ** 如果没有可复用的Connection,则创建一个 **/ if (!foundPooledConnection) { if (selectedRoute == null) { selectedRoute = routeSelection.next(); } // Create a connection and assign it to this allocation immediately. This makes it possible // for an asynchronous cancel() to interrupt the handshake we're about to do. route = selectedRoute; refusedStreamCount = 0; result = new RealConnection(connectionPool, selectedRoute); acquire(result, false); } /** ** RealConnection的connect方法连接服务器 **/ // Do TCP + TLS handshakes. This is a blocking operation. result.connect( connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, connectionRetryEnabled, call, eventListener); routeDatabase().connected(result.route()); /** ***省略一些代码 **/ return result; }
CallServerInterceptor
请求拦截器,真正发起网络请求,并获得Response。
Application Interception
应用拦截器,是okhttp最先调用的拦截器,即上面代码中的client.interceptors()。
因为在最顶层,所以即使是缓存的请求也会通过该拦截器。
一般会通过该拦截器进行一些拦截操作。
Network Interception
网络拦截器,最终网络请求前执行的拦截器,即上面代码中的client.networkInterceptors()。
由于该拦截器发生在真正网络请求的拦截器前,所以只会在真正发生网络请求时才会调用,并且
response 时网络数据还没有经过解析,比较难读。一般除非需要对网络数据进行操作,不会使用该拦截器。
连接池
ConnectionPool
连接池管理所有客户端和服务端的连接,实现连接复用,减少 TCP 三次握手四次分手频率。
创建
OkhttpClient 类的 Builder 模式中创建实例:
connectionPool = new ConnectionPool();
/** * Create a new connection pool with tuning parameters appropriate for a single-user application. * The tuning parameters in this pool are subject to change in future OkHttp releases. Currently * this pool holds up to 5 idle connections which will be evicted after 5 minutes of inactivity. */ public ConnectionPool() { this(5, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES); } public ConnectionPool(int maxIdleConnections, long keepAliveDuration, TimeUnit timeUnit) { this.maxIdleConnections = maxIdleConnections; this.keepAliveDurationNs = timeUnit.toNanos(keepAliveDuration); // Put a floor on the keep alive duration, otherwise cleanup will spin loop. if (keepAliveDuration <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("keepAliveDuration <= 0: " + keepAliveDuration); } }
创建最大连接数5,KeepAlive 时间5分钟的 ConnectionPool。
ConnectionPool 中有一个重要的变量:executor
/** * Background threads are used to cleanup expired connections. There will be at most a single * thread running per connection pool. The thread pool executor permits the pool itself to be * garbage collected. */ private static final Executor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0 /* corePoolSize */, Integer.MAX_VALUE /* maximumPoolSize */, 60L /* keepAliveTime */, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp ConnectionPool", true));
放入连接
void put(RealConnection connection) { assert (Thread.holdsLock(this)); if (!cleanupRunning) { cleanupRunning = true; executor.execute(cleanupRunnable); } connections.add(connection); }
cleanupRunning 用来清理空闲线程。
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { while (true) { long waitNanos = cleanup(System.nanoTime()); if (waitNanos == -1) return; if (waitNanos > 0) { long waitMillis = waitNanos / 1000000L; waitNanos -= (waitMillis * 1000000L); synchronized (ConnectionPool.this) { try { ConnectionPool.this.wait(waitMillis, (int) waitNanos); } catch (InterruptedException ignored) { } } } } } };
不停的调用 cleanup 方法清理空闲连接,wait 方法设置间隔时间。
cleanup 方法中采用引用计数的方式统计空闲/活跃连接词。
上文中提到的 StreamAllocation 对象即为计数对象。
获取连接
/** * Returns a recycled connection to {@code address}, or null if no such connection exists. The * route is null if the address has not yet been routed. */ @Nullable RealConnection get(Address address, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, Route route) { assert (Thread.holdsLock(this)); for (RealConnection connection : connections) { if (connection.isEligible(address, route)) { streamAllocation.acquire(connection, true); return connection; } } return null; }
遍历 connections,查看是否存在可复用的连接。
移除连接
/** * Notify this pool that {@code connection} has become idle. Returns true if the connection has * been removed from the pool and should be closed. */ boolean connectionBecameIdle(RealConnection connection) { assert (Thread.holdsLock(this)); if (connection.noNewStreams || maxIdleConnections == 0) { connections.remove(connection); return true; } else { notifyAll(); // Awake the cleanup thread: we may have exceeded the idle connection limit. return false; } }
移除所有连接
/** Close and remove all idle connections in the pool. */ public void evictAll() { List<RealConnection> evictedConnections = new ArrayList<>(); synchronized (this) { for (Iterator<RealConnection> i = connections.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) { RealConnection connection = i.next(); if (connection.allocations.isEmpty()) { connection.noNewStreams = true; evictedConnections.add(connection); i.remove(); } } } for (RealConnection connection : evictedConnections) { closeQuietly(connection.socket()); } }
连接池总结
Deque\<RealConnection\> 存储连接,通过上述四个方法操作连接池,StreamAllocation 计数是否回收连接。
